Table of Contents
- Towards Sustainable Mobility: Optimization and Comfort in Public Transportation
- The Added Value of AI
- An Ambitious and Challenging Project
- Future Developments
Thanks to an AI project, Neodata has helped improve urban transportation in a major city, increasing environmental sustainability and offering a better travel experience for passengers.
Urban mobility is a broad and multifaceted issue that presents numerous opportunities for AI to effectively support the planning and continuous improvement of various aspects, such as network optimization (routes, schedules, vehicles), service quality, revenue, and other commercial aspects.
This article discusses the Smart Bus Path project, a collaboration between Neodata and its partner SmartME, involving the transport companies of two major Italian cities (whose names and results will be published upon project completion).
Towards Sustainable Mobility: Optimization and Comfort in Public Transportation
The focus is on urban mobility, primarily in two areas:
The first is the collection and analysis of passenger numbers. The project involves precisely monitoring the number of passengers boarding and alighting at each stop, for each line and bus trip, concerning vehicle capacity. The goal is to use available vehicles based on the actual needs of users, adjusting the frequency or capacity of trips throughout the day to avoid overcrowded buses on one hand and nearly empty trips on the other.
One of the platform’s initial achievements is optimizing trips and eliminating unnecessary ones, with the added benefit of reducing pollution, besides the evident economic advantages.
The second focus is on the passenger experience, which extends beyond bus crowding. It includes a broader measure of travel experience that takes into account other parameters—detected by specific sensors—such as air quality on board, noise, punctuality, seat availability, and the driver’s driving style.
The Added Value of AI
In the previously described process, the added value of using Artificial Intelligence impacts various aspects, such as simulating possible scenarios. This allows for identifying corrective actions to achieve an improved or optimal situation.
Urban transportation is a complex system with non-linear relationships and only sometimes straightforward cause-and-effect dynamics. Any action that alters the system can generate unpredictable effects on other factors, which need to be anticipated and considered in advance. This is where the great value of scenario simulation lies.
The technology employed includes the production, collection, and processing of a vast amount of data from highly heterogeneous sensor systems: from those already present on vehicles to additional ones provided by SmartME in this project.
Moreover, particular attention has been given to the User Experience, making the daily operation of the platform users—namely, bus network planners—not only simple but effective in identifying necessary actions and evaluating their real effects.
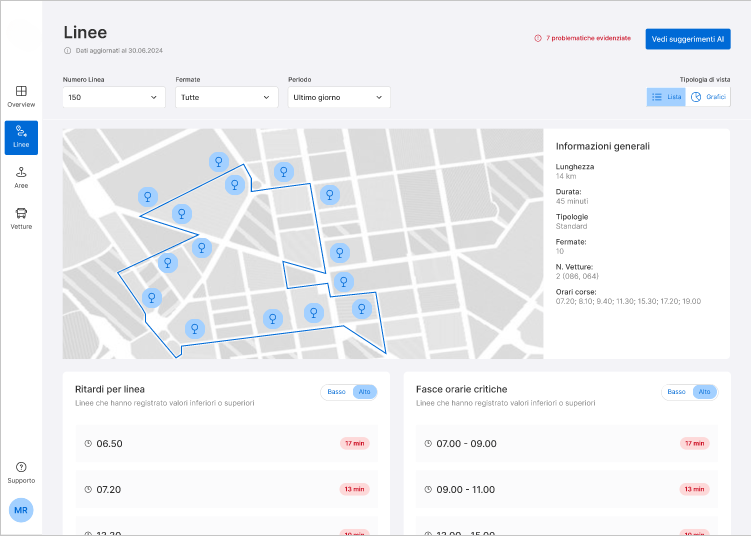

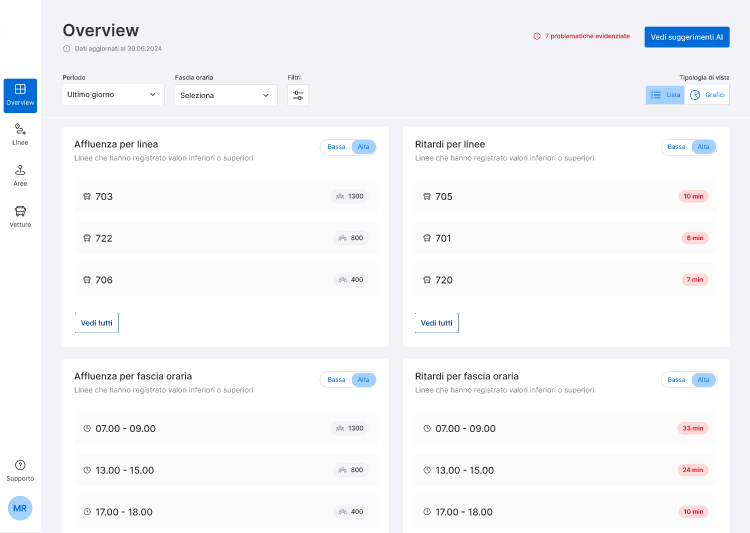
An Ambitious and Challenging Project
“The collection of requirements and the creation of a sufficiently flexible data model to meet them is currently the most challenging aspect of the project” says Tiziana Zapperi, head of the technical team. “The challenge is to combine the theoretical solutions of Data Science with the real needs gathered from pilot cases, to meet these needs while also creating a general-purpose platform ready for the needs of other potential companies that will adopt the system.”
“The objective Neodata sets for this project is to improve various aspects of municipal companies and, consequently, ensure that technology has a direct and clear effect in improving the lives of hundreds of thousands of people” declares Dino De Luca, Chief Growth Officer of Neodata. “But our ambition on this topic goes further: the data collected during the trial period, as well as the way our platform will be validated and improved by real use, will provide compelling arguments for other cities to adopt our technology.”
Future Developments
The project might include a second phase that involves using the same data collection infrastructure but with a different perspective: that of urban area managers. The sensors on buses can be extended to collect data not only inside the vehicles but also externally, at various points in the city they traverse.
The result is a mobile sensor network, significantly fewer than required for fixed sensors, which, when appropriately interpolated, can offer a detailed mapping of urban livability parameters such as air quality, noise, traffic conditions, temperature/humidity, etc. Thus, a smart city platform is in the hands of municipal administrations to analyze and improve the quality of life for citizens.
The objective is to complete the development and trial phase effectively and connect with other municipal administrations and urban transport companies to gather further ideas and requirements, making this platform increasingly aligned with the needs of businesses and citizens.
Contact us at info@neodatagroup.ai to discover together how to shape the cities of the future.

Neodata AI Team
As Neodata, we provide data, insight, articles, and news related to AI and Big Data.
-
Neodata AI Team#molongui-disabled-link
-
Neodata AI Team#molongui-disabled-link
-
Neodata AI Team#molongui-disabled-link
-
Neodata AI Team#molongui-disabled-link