Table of Contents
Which countries are leading the race in artificial intelligence? The British magazine Tortoise recently published the 2024 Global AI Index, which ranked the 83 countries investing in AI to determine who best leverages this technology’s potential. This article will explore the countries to watch and how Italy can strengthen its position in this landscape.
The Study
Now in its fifth edition, this year the index expands the list of countries examined to 83, with new indicators. The ranking considers 122 different indicators covering topics such as talent, infrastructure, the operating environment, research, development, business ecosystem, and government strategy, grouping them into three pillars of analysis: implementation, innovation, and investment, which are further broken down into seven sub-pillars as follows:
- Talent (Implementation): This sub-pillar assesses the availability of skilled AI professionals, examining the education, expertise, and experience of specialists and researchers. Having a robust talent pool is essential for developing advanced AI solutions.
- Infrastructure (Implementation): Infrastructure evaluates the capacity and scale of computational resources, including advanced computing systems and semiconductor manufacturing. This technological foundation is crucial for building and managing AI applications that require large data processing capabilities.
- Operational Environment (Implementation): This sub-pillar looks at the regulatory context and public perception of AI. It considers how laws, regulations, and citizen views impact AI development and adoption across sectors.
- Research (Innovation): Research assesses the quantity and quality of academic and industry contributions to AI. The publication of studies and the participation of research institutions are at the core of innovation, providing new insights and applicable technologies.
- Development (Innovation): Development focuses on creating new AI models and applied innovation through patents across various fields. This is a key factor in creating new AI tools and technologies that can be adopted and transformed into practical solutions.
- Government Strategy (Investment): Government strategy measures public investment and national initiatives to promote and support AI. This sub-pillar reflects a country’s commitment to positioning itself as a leader in the AI sector.
- Commercial Ecosystem (Investment): The commercial ecosystem reflects the level of AI-related economic activity, including private investment, startups, and corporate initiatives. A vibrant and well-supported ecosystem is essential for turning AI innovations into real value and economic development.
The Ranking
The United States tops the ranking with a significant lead, scoring 100 points, compared to China’s 53 in second place. The following eight top countries are closely grouped, with scores ranging from 32 to 23. Italy ranks 24th with a score of 15.8, trailing behind other major European Union nations.
Singapore holds steady in third place, affirming its role as Asia’s leading AI center after China. The nation scores exceptionally well on relative measures, such as the number of AI researchers per million residents. However, it has also made significant strides in absolute metrics, particularly in AI research and funding.
The UK retains its fourth-place position, though just barely, as France is quickly closing in. While the UK maintains an edge in commercial AI, France is now surpassing it in areas like open-source large language model (LLM) development, public investment, and computing resources. France has risen to fifth place, marking its debut in the global top five AI leaders.
The Italian Situation
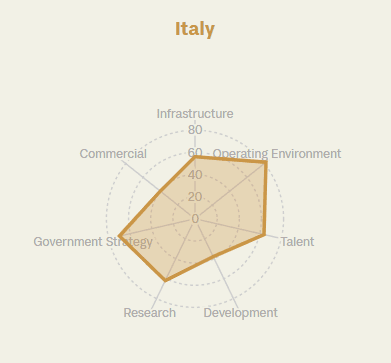
Despite its overall ranking, Italy stands out in certain specific indicators examined in the study. Notably, the country ranks first for its operating environment, which assesses the regulatory context and public opinion regarding artificial intelligence. In recent months, awareness and confidence in AI have grown, fueling a perception of AI as a potential driver of productivity—a challenge that has affected Italy’s economy for years. Additionally, strategies promoted by the government position Italy just outside the top 10 in this category.
However, underperformance in development and commercialization negatively impacted Italy’s overall score. These categories include indicators such as support for startups, private investment, and AI-related commercial initiatives, areas in which the country still has significant room for improvement.
Recommendations for the Future
To improve its standing in the global AI landscape, Italy should focus on:
- Training and attracting talent: Invest in specialized educational programs and create opportunities to attract skilled professionals.
- Strengthening technological infrastructure: Develop supercomputing centers and support local production of advanced technology components.
- Updating the regulatory framework: Adopt laws that facilitate AI adoption while ensuring data protection and security.
- Increasing R&D investment: Encourage high-quality study publications and promote participation in international projects.
- Defining a clear government strategy: Set concrete goals and allocate adequate resources to promote AI development.
- Stimulating the commercial ecosystem: Offer tax incentives and create tech hubs to foster innovation and collaboration among businesses.
With a strategic focus on these areas, Italy can enhance its position and impact in the evolving global AI landscape.
Neodata AI Team
As Neodata, we provide data, insight, articles, and news related to AI and Big Data.
- Neodata AI Team#molongui-disabled-link
- Neodata AI Team#molongui-disabled-link
- Neodata AI Team#molongui-disabled-link
- Neodata AI Team#molongui-disabled-link